Table of Contents
The Synology SSD Cache is a device that caches and stores data on your NAS.
This cache allows you to enjoy high application acceleration performance across all applications and greatly improve the overall system performance.
This article will give you a good understanding of whether the Synology SSD Cache is worth your money and if it’s something you should invest in yourself.
The SSD drive has been a wonderful upgrade in storage capability and response when it needs to be able to read fast and work faster. For example, the improvement seen in SSD drives with operating systems and high-processing games has been significantly greater than anything a traditional hard drive could produce.
What’s the difference between SSDs and other hard drives?
The beauty of the SSD is its architecture. Instead of relying on moving parts to lay data into a storage medium that is then preserved for as long as the disk functions, spins, and can be read, the SSD has no moving parts whatsoever. Instead, it utilizes flash memory, coding data electronically into the chips at lightning speed (as fast as 2.2GB/sec). The process and stability are entirely electronic, without any mechanical motion at all. For a unit that needs to operate heavily with random access memory during use, the SSD is a recommended advantage over any other kind of storage.
Unlike traditional systems, however, SSD caches have the unique advantage that what is worked on is actually saved. So, if the system suffers a power outage or disconnect, the work in random access memory is preserved and not lost. The same can’t be said for traditional architecture.
What is the SSD cache on the Synology NAS?
An SSD cache is a feature on the Synology NAS that allows users to access data from their solid state drives faster. This can be beneficial for data storage, especially when it comes to large files and media files. This speeds up overall NAS performance and makes it easier for users to access their data quickly.
The M2 NVMe SSD device can be accessed more quickly than its larger counterparts, but this comes with higher storage costs on each drive in comparison to HDD or SSD devices.
SSD caching is the process of temporarily storing data on an SSD drive in order to make it more quickly accessible. When a program is run, the operating system will first look for and access this cached data before accessing the hard disk drive. This speeds up how long programs take to load because they do not need to wait while searching through all of the files on your computer’s hard drives.
Caching uses the high-speed SSD drive to provide quick read and write speeds and can be configured by setting how much of your hard drive data will be cached.
Unfortunately, caching is an expensive option, but it provides significant performance boosts in applications where speed plays a role. In some cases, this might not be worth its price point because the performance boost does not outweigh its cost.
How does SSD caching work?
The SSD cache is a feature of the Synology DiskStation. It uses an SSD and RAM to load files from one or more storage drives, which are then cached in the hard drive’s RAM. This allows files that may be needed for execution to be loaded quickly and reliably by using less power than if they were being accessed directly from the disk drives.
In the example shown, fast-responding files go straight to the CPU cache while slower-responding data goes to RAM. Then – at least in this example – the hard drive comes up last and all of it is written back out as quickly as possible, which means that there’s less waiting time for a file on your PC.
The Synology SSD Cache has a lot of benefits: it uses very little power from your computer, you can configure how many read and write operations are processed, and it can help your Synology boot up faster.
The Synology SSD Cache is a device that allows users to increase the performance of their NAS by adding an external storage drive. With this data request, overall computing performance will be dramatically faster because it can handle both read and write requests at the same time, which are processed on separate cores in parallel.
This product has a high price tag, but many people have found its value well worth it for those who need fast disk drives or want more reliable ones for mission-critical workflows.
Why do you need an SSD cache?
When using an SSD cache, the goal is to use it most for those functions that need to rapidly keep accessing the same data files or small portion of data storage quickly. This is common with e-commerce systems accessing a shopping catalog, data processing functions referencing tables for transactions, and stock market systems running and referencing repeated correlations with changing market data and positions. Other similar examples are slowed by traditional hard drive storage or limited by similar stock motherboard memory. The SSD cache takes this load from a server and instead smooths out the processing demand so that the rest of the system is not being slowed by it.
How to set up SSD cache on Synology NAS
- Turn off your Synology
- Install your SSD into your Synology
- Turn your Synology back on
- Access your Synology DSM
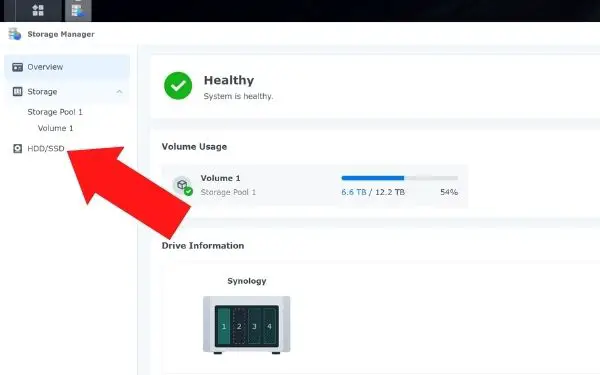
- Click on Main Menu on the top left of the desktop

- Click on Storage Manager

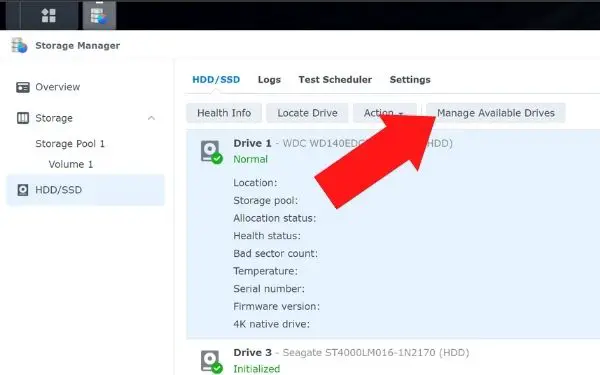
- Click on HDD/SSD

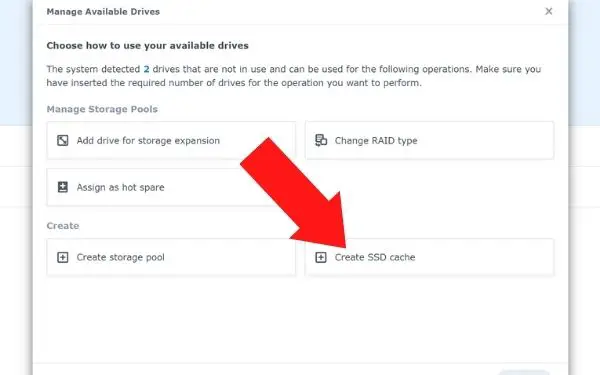
- Click on manage available drives

- Click on create SSD cache

- Select the cache mode
- Select the volume you want the SSD cache to mount on
- Select the SSD you installed from the list
- Click Apply
Not all SSDs are the same
There are limitations to using a Synology SSD cache that one should be aware of when applying the system. Not every SSD drive can be used with it. Specific models need to be matched to the SSD cache, and it has a size limitation as well. Not only will incompatible hardware create glitches and delays, but data files could be damaged or lost as well.
Synology SSD caches can be powerful additions to a robust network system, but they have to be used correctly. Matching the SSD cache with the correct hardware ensures they work correctly and, most importantly, protects the active work you need an SSD cache to perform.
How to choose the size of a SSD
Two styles of SSD caches are typically used, both with their advantages and matched to the functional needs of a network. The first is a read-only style cache, which is set to provide maximum fast referencing and reading of existing files without changes or modifications. These can be as big as 12 SSDs or as small as one drive. The second style of approach is a read-write system where there is an extensive amount of reading and modification happening with high frequency. Again, this can be as large as 12 drives or as small as two.
The SSD Cache Advisor is a free tool that provides an indication of whether the workload will benefit from using a Synology with SSD cache. It also gives recommendations on how to configure the cache size and whether or not to use RAID when set at higher capacities.
If you’re considering buying a new NAS device, this tool could help make your decision easier.
In order to determine the size of an SSD cache on NAS, it’s important that you understand how they are configured. A Synology SSD cache is available in 2 sizes and can be configured through the storage manager or with command line commands. In this set up, we recommend the storage manager method because it’s the fastest and easiest.
The price difference between the two configurations is minimal, so this decision comes down to preference or whether your device supports them at all!
The disadvantages of having an SSD cache
SSD cache systems do not work well when a heavy file is loaded and then processed through sequentially without returning for more referencing. This would be the case with video-streaming, for example, or one-time passes on large files. Protein folding, on the other hand, would benefit tremendously from the architecture. Fortunately, SSD cache systems have the ability to pass through such large files to traditional resources and not waste SSD resources on them as well, a unique and beneficial feature included with Synology SSD caches.
In addition, SSDs and SSD caches do have another Achilles heel. Unlike regular hard drives, they lose the ability to access their data when they begin to suffer critical failure. To offset this eventual risk, Synology SSD caches include programming to auto-protect themselves when degradation starts to occur. Synchronization is set to an existing network hard drive, and the SSD bars any further storage on itself. This prevents increasing asset loss size and preserves the current data for the SSD replacement.
Other interesting articles: